本文简要介绍了C/C++ ABI(Application Binary Interface)兼容性,及其在插件方面的实现指引和方法。在当今热火的AIoT(人工智能物联网)领域,智能模块的C/C++插件化,是开发方式的主流。AIoT的算法场景众多,需求不断增长,每个场景的客户需求又各不相同,且随着认知的加深在不断变化。限于AIoT边缘计算设备的特殊性,比如使用流量卡与云端互联,升级条件复杂,成本较高,随着版本的迭代和客户的增加,升级任务也日趋碎片化。不管是客户的需求更新,还是算法的优化,都要求智能模块可以进行简易快速的升级。
1. 前言
为了达成这样的目的,DeepStream的框架设计就显得特别友好,DeepStream将智能应用与平台独立开来,每一个模块由APP+Plugin组成。APP调用Plugin完成数据预处理、推理任务、结果后处理、结果分析、显示和上报等任务。国内的智能平台提供商,也在纷纷模仿DeepStream,期望开发一套同样强大的智能化推理平台。
二进制兼容性意味着用户只需要重新链接新版的静态库或者将新版的动态库放在库路径替换,应用程序能正确运行并获得新的功能或者Bug修复。相比之下,源码兼容性则需要客户在获得新版的库代码后,重新编译应用程序。 具体的来说,API的修改不应该改变类、方法或函数在库中的表示,所有类型、大小、结构体对齐和所有的函数签名都应当维持原样。但是,C++没有给出相关的ABI规范,每一个编译器的处理方式都是不尽相同的。
C++存在Name Mangled,函数名会被重新修饰为一堆莫名其妙的表示;C++的调用方式类似一种“偏移量”的方式定位被调用对象,比如虚函数,结构体成员,一旦我们修改了布局很可能让程序“找错位置”。C++的特殊性使得调用方无法确切的进行调用,一不小心就会破坏ABI兼容性。于是,人们给出了C++保持ABI兼容的API修改方法,以及破坏ABI兼容性的API修改方法。虽然我们尽量保持ABI兼容性,但是仍然很难保证不出意外。为了检验和保证ABI兼容,我们应当使用ABI检查工具进行把关,同时还应当引入完整的API修改的审核机制。
2. ABI兼容的合法和非法行为
2.1. What’s allowed
Note that this may not be an exhaustive list. Anything with a large caveat has not been included.
You can…
- Add new non-virtual functions
- Add a new enum to a class
- Append new enumerations to an existing enum
- Remove private non-virtual functions if they are not called by any inline functions (and never have been)
- Remove private static members if they are not used by any inline functions (and never have been)
- Add new static data members
- Add new classes/structs
- Add or remove friend declarations to classes
2.2. What’s not allowed
Note that this may not be an exhaustive list. There may be things not on this list that cause an ABI breakage.
You cannot…
- For an existing class or struct
- Remove the class
- Change a class hierarchy in any way (add, remove or reorder base classes)
- Change class template arguments in any way, including adding an argument with a default value
- Add new non-static data members, even if they are protected or private
- Remove existing data members
- Change the order of declaration of non-static data members, even if they are protected or private
- Change the type of a data member
- For an existing function of any type
- Remove it
- inline it (this includes moving a member function’s body to the class definition, even without the inline keyword)
- Add an overload, if that function did not already have at least one overload
- Change its signature in any way. This includes:
- Adding a parameter, even if it has a default value
- Removing a parameter, even if it has a default value
- Changing the type of any of the parameters, including const/volatile qualifiers
- Changing the return type in any way
- Changing the const/volatile qualifiers of a member function
- Changing the access rights to functions or data members, for example from public to private. If you need to make a private function protected or public, add a new function that calls the private one.
- If inline, make certain changes to its implementation
- For virtual member functions
- Add new virtual functions
- Change the order of virtual functions in the class declaration
- Override an existing virtual function if that function is not in the top-level base class that has virtual functions
- Override an existing virtual function if it has a covariant return type [5]
- Remove a virtual function, even if it is a reimplementation of a virtual function from the base class
- For static non-private members or global variables
- Remove it
- Change its type
- Change its const/volatile qualifiers
- Change #defined constants
- For enumerations
- Change values of members
- Remove members
- Add members anywhere but the end of the list
- Rename members
- Change function calling conventions [同一平台、同一种编译器、应当不会触发cdecl问题]
3. ABI兼容性检查工具介绍
ABI Compliance Checker就给了我们很好的帮助,同时提供了ABI兼容性检查结果和Source兼容性检查结果,后面介绍该工具的使用方法。
Android SDK则使用了libabigail对kernel进行ABI兼容性检查。
ABI Compliance Checker 主页后面提供了很多非常有价值的参考文章,介绍了ABI兼容性和如何实现ABI兼容性。
ABI Compliance Checker的使用有两种方法,一种是源码编译,另一种是在linux上直接通过apt-get 安装工具。
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install vtable-dumper abi-dumper abi-compliance-checker -y
先研究它的Test Suite,非常值得参考:
abi-compliance-checker -test
执行后在当前目录得到一个test目录,里面包含了源码和兼容性检查结果。该Test Suite展示了100项C API/ABI兼容性问题和200项C++ API/ABI兼容性问题。
同时,生成的test目录下面还有工具的使用示例,参照该示例和abi-compliance-checker 代码库中的doc目录,能非常容易的将工具应用到实际项目中。
下面一份该工具的生成结果:
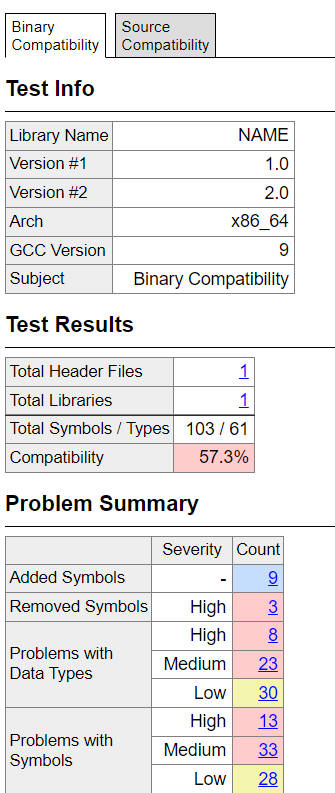
4. 怎么做到ABI兼容
使用dlopen动态加载,这方面的知识就不介绍了,下面主要是ABI兼容方面的说明。
4.1. 使用C Style封装接口
由于C++不容易实现ABI兼容,我们应当使用C API style作为库的API接口样式(纯C API),在接口外围添加:
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
// C CPI 声明
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
将C++接口进行C style封装后,我们要做的事情就少了很多,降低了实现ABI兼容的门槛。可以参考DeepStream,或者其它C++ 库,API都是这么做的,好处就不言而喻了。最直接的好处是,它能保持API名称的不变,避免被进行Name Mangled。
缺点也很明显,我们无法在API处使用C++的特性(比如类、继承、模板、泛型、函数式等)。要知道,使用C++ API实现ABI兼容,是极其困难的。如果开发团队足够强大,同时提供C API和C++ API也是可以的。
4.2. 尽量使用原始数据类型
在接口处,尽量使用原始数据类型,少用struct(C/C++)、对象(C++)等来传参。比如使用struct传参,struct的约束就非常多:
- struct中不要删除成员(导致后续成员”偏移量”改变);
- 不能调整成员的相对位置(导致成员”偏移量”改变);
- 只能以追加的方式增加成员;
- 不要轻易修改成员的类型;
- 新增的成员只能在新的内部函数中使用(人不是机器,这样做总是会难以预料地出现ABI兼容性问题,编译没事,但功能不正确,甚至线上crash)
- 尽量不要使用Aggregate initialization;
- 不要使用menset、memcpy、sizeof操作;
- 很多。。。
总结起来就一句话:不要轻易改变其大小和布局。
对于struct,最佳方案应当是新增一个struct,比如对struct A修改后,新增struct AEx在新的版本中发布出来。
4.3. 接口处的对象由库全权把持所有权
当我们需要创建对象时,提供API进行创建,并提供该对象的管理机制,可以是提供API进行释放,也可以是API调用结束或者在析构函数中手动释放。总之,要保证库函数完全负责对象的创建和销毁。
举个例子:
lib_v1通过API返回一个结构体的共享指针shared_ptr of struct A,给到App外面。App拿着这个共享指针(普通指针类似),当App释放该struct时,是以App看到的struct结构进行释放。
假设,我们在struct A中追加了一个成员b,并升级lib_v2。App没有重新编译,App编译时的头文件中struct A中没有成员b。当App使用到lib_v2时,释放struct A,b没有被释放。存在内存泄漏的隐患。
同样的,如果struct A中删除了一个成员,虽然我们再三确认App没有调用这个成员,并勇敢地删除了,一切看起来没有问题。但App释放该struct时,会将删除的这个成员的位置也释放掉。 另外,如果是App有操作尝试写入的struct A中删除的成员,则很可能导致程序跑飞。
所以,最好的方式是,库开发者提供API来操作struct A,除了创建和释放,还包括读取和赋值,库开发者负责这些API的ABI兼容性。
每一个操作特定数据结构的API都应当有特殊醒目的关键字,比如操作struct A,可以是MyPluginStructAModify。
4.4. 建立完整的API审核机制
首先,我们应当使用ABI checker来进行严格把关,不允许出现High Severity问题,其它低等级的Severity问题应当严格进入人工审核,由经验丰富的长者或者开发者之间进行相互审核。
同时,代码审核机制应当完备,严格遵循API设计规范、提供完备的注解和API文档(借助Doxygen工具),具有完备的代码审核流程。
最后,应当有丰富和完备的测试用例,在发布新版API时,同时在新旧平台上利用新旧APP进行符合ABI兼容性测试,所涉及的范围应当是新版本库指定的兼容范围。
4.5. 建立灵活的升级机制
提供灵活的APP升级和库(插件)升级机制,有时候,库的API很难做到完全兼容,必要时需要APP也进行同时升级。升级模块应当能处理好APP和库之间的依赖关系,自动完成依赖检查和错误纠正。
5. 一些实现C++ ABI的实践参考
除了C Style API,如果需要实现C++ ABI,我们应该如何着手?
文章说明了C++虚函数的弊端,以及COM通过继承的方式拓展接口的弊端,表扬了Linux Kernel通过系统调用的方式保持接口的不变性,并说明了Pimpl方式实现接口的好处。 并说明了非虚函数的健壮性: virtual function 是 bind-by-vtable-offset,而 non-virtual function 是 bind-by-name。 最后,作者提供了一个推荐做法:
- 使用Pimpl包装实现,将实现代码完全转移到so中,二进制随着库升级自动变更;
- class内的API不使用虚函数,可以灵活在新版本中添加新的函数;
类似于Pimpl,D-Pointer也是将实现细节完全隐藏在库内的接口设计方式。Qt因此而具有非常好的ABI兼容性,即使我们将使用底版本(比如Qt4.5)编译的App,也能在高版本(比如Qt4.6)库中正确运行。
d-pointer的思想是,在导出类中保存一个私有类/数据结构的指针,这个私有的类的子类可以自由的变更,而不会对APP产生副作用,对于APP来说,d-pointer只是一个指针,导出类的大小没有变化,所以不存在ABI问题。
上面提到的私有类的子类,虽然可以在内部自由变化,但是我们需要将这个d-pointer转换到其对应的子类,以及相互转换。这时,Qt内部就提供了便捷的宏(Q_D和Q_Q。Q_DECLARE_PRIVATE和Q_DECLARE_PUBLIC)来完成这个事情。
6. 参考
《C++ API设计》
《ABI Compliance Checker》