在FrameTimeline相关的文章中,Jank类别对应应用绘制部分的分类比较粗糙,仅仅是笼统地给出AppDeadlineMissed,有没有更详细的应用绘制追踪和Jank分类呢。
JankTracker
在 CanvasContext::CanvasContext() 构造函数中创建JankTracker对象,mJankTracker(&thread.globalProfileData())。
JankTracker主要的函数与成员变量:
class JankTracker {
FrameInfo* startFrame() { return &mFrames.next(); } // 一帧的开始,开始渲染时
void finishFrame(FrameInfo& frame...); // SurfaceFlinger latchBuffer回调
void calculateLegacyJank(FrameInfo& frame); // 与finishFrame,共同完成对Jank类型的计算
RingBuffer<FrameInfo, 120> mFrames; // 可以至少保存1秒的帧信息,120hz刷新率时
}
FrameInfo其实仅仅是一个int64_t数组,下标表示某种时间,数组的值表示具体的时间值。
class FrameInfo {
const int64_t* data() const { return mFrameInfo; }
int64_t mFrameInfo[static_cast<int>(FrameInfoIndex::NumIndexes)];
}
CanvasContext维护了一个FrameInfo变量,mCurrentFrameInfo,FrameInfo都是在ConvasContext中填充的。
void CanvasContext::prepareTree(TreeInfo& info, int64_t* uiFrameInfo, int64_t syncQueued,
RenderNode* target) {
// If the previous frame was dropped we don't need to hold onto it, so
// just keep using the previous frame's structure instead
if (!wasSkipped(mCurrentFrameInfo)) {
mCurrentFrameInfo = mJankTracker.startFrame(); // 获取FrameInfo对象
}
mCurrentFrameInfo->importUiThreadInfo(uiFrameInfo); // 同步UiThread的时间信息
mCurrentFrameInfo->set(FrameInfoIndex::SyncQueued) = syncQueued;
mCurrentFrameInfo->markSyncStart();
}
先是同步了UiThread的时间信息,然后设置Sync开始时间。UiThread时间信息在前面一点的位置填充:
void CanvasContext::prepareAndDraw(RenderNode* node) {
ATRACE_CALL();
nsecs_t vsync = mRenderThread.timeLord().computeFrameTimeNanos();
int64_t vsyncId = mRenderThread.timeLord().lastVsyncId();
int64_t frameDeadline = mRenderThread.timeLord().lastFrameDeadline();
int64_t frameInterval = mRenderThread.timeLord().frameIntervalNanos();
int64_t frameInfo[UI_THREAD_FRAME_INFO_SIZE];
UiFrameInfoBuilder(frameInfo)
.addFlag(FrameInfoFlags::RTAnimation)
.setVsync(vsync, vsync, vsyncId, frameDeadline, frameInterval);
TreeInfo info(TreeInfo::MODE_RT_ONLY, *this);
prepareTree(info, frameInfo, systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC), node);
if (info.out.canDrawThisFrame) {
draw();
} else {
// wait on fences so tasks don't overlap next frame
waitOnFences();
}
}
prepareAndDraw提供了mFrameInfo前面部分的时间信息,剩下部分由CanvasContext填充。
nsecs_t CanvasContext::draw() {
mCurrentFrameInfo->set(FrameInfoIndex::FrameInterval) =
mRenderThread.timeLord().frameIntervalNanos();
mCurrentFrameInfo->markIssueDrawCommandsStart();
const auto drawResult = mRenderPipeline->draw(frame, windowDirty, dirty, mLightGeometry,
&mLayerUpdateQueue, mContentDrawBounds, mOpaque,
mLightInfo, mRenderNodes, &(profiler()));
uint64_t frameCompleteNr = getFrameNumber();
waitOnFences();
if (mNativeSurface) {
if (vsyncId != UiFrameInfoBuilder::INVALID_VSYNC_ID) {
native_window_set_frame_timeline_info(
mNativeSurface->getNativeWindow(), vsyncId, inputEventId,
mCurrentFrameInfo->get(FrameInfoIndex::FrameStartTime));
}
}
bool didSwap = mRenderPipeline->swapBuffers(frame, drawResult.success, windowDirty,
mCurrentFrameInfo, &requireSwap);
mCurrentFrameInfo->set(FrameInfoIndex::CommandSubmissionCompleted) = std::max(
drawResult.commandSubmissionTime, mCurrentFrameInfo->get(FrameInfoIndex::SwapBuffers));
SwapHistory& swap = mSwapHistory.next();
swap.swapCompletedTime = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
swap.vsyncTime = mRenderThread.timeLord().latestVsync();
swap.dequeueDuration =
ANativeWindow_getLastDequeueDuration(mNativeSurface->getNativeWindow());
swap.queueDuration =
ANativeWindow_getLastQueueDuration(mNativeSurface->getNativeWindow());
mCurrentFrameInfo->set(FrameInfoIndex::DequeueBufferDuration) = swap.dequeueDuration;
mCurrentFrameInfo->set(FrameInfoIndex::QueueBufferDuration) = swap.queueDuration;
mCurrentFrameInfo->markSwapBuffersCompleted();
reportMetricsWithPresentTime();
FrameMetricsInfo& next = mLast4FrameMetricsInfos.next();
next.frameInfo = mCurrentFrameInfo;
next.frameNumber = frameCompleteNr;
next.surfaceId = mSurfaceControlGenerationId;
return mCurrentFrameInfo->get(FrameInfoIndex::DequeueBufferDuration);
}
draw()函数里面填充了mRenderPipeline的draw过程和swapBuffer过程的时间。同时,通过ANativeWindow接口从Surface获取到DequeueBuffer和QueueBuffer的耗时。
随机将mCurrentFrameInfo保存到mLast4FrameMetricsInfos中,最多缓存4个最近的FrameInfo。
draw()其实完全统计了RenderThread渲染流程的耗时,如下图:
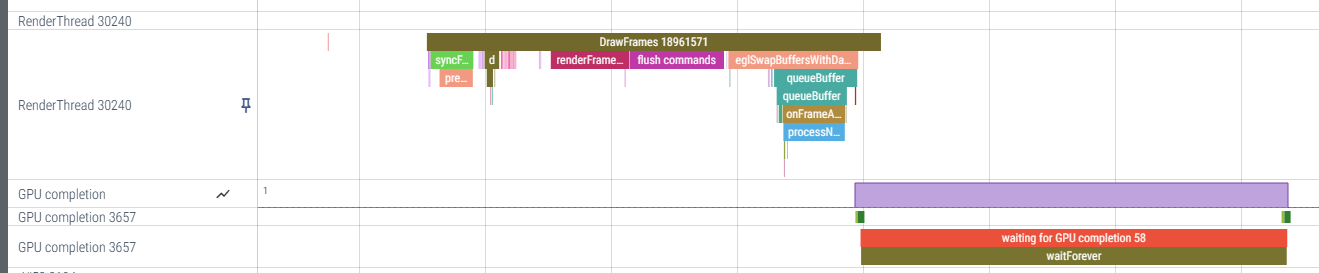
但是GPU completion线程的时间还未得到,因为不可能提前只是GPU何时完成实际的渲染工作。这个其实是从SurfaceFlinger回调过来的。
void CanvasContext::onSurfaceStatsAvailable(void* context, int32_t surfaceControlId,
ASurfaceControlStats* stats) {
auto* instance = static_cast<CanvasContext*>(context);
const ASurfaceControlFunctions& functions =
instance->mRenderThread.getASurfaceControlFunctions();
nsecs_t gpuCompleteTime = functions.getAcquireTimeFunc(stats); // 获取acquireFence的时间
if (gpuCompleteTime == Fence::SIGNAL_TIME_PENDING) {
gpuCompleteTime = -1;
}
uint64_t frameNumber = functions.getFrameNumberFunc(stats);
FrameInfo* frameInfo = instance->getFrameInfoFromLast4(frameNumber, surfaceControlId); // 获取缓存的FrameInfo
if (frameInfo != nullptr) {
frameInfo->set(FrameInfoIndex::FrameCompleted) = std::max(gpuCompleteTime,
frameInfo->get(FrameInfoIndex::SwapBuffersCompleted)); // 从swapBuffer完成与acquireFence中取一个最大值
frameInfo->set(FrameInfoIndex::GpuCompleted) = std::max(
gpuCompleteTime, frameInfo->get(FrameInfoIndex::CommandSubmissionCompleted)); // 从命令提交完成时间和acquireFence中去一个最大值
std::scoped_lock lock(instance->mFrameMetricsReporterMutex);
// 通知JankTracker进行信息统计和Jank类型计算
instance->mJankTracker.finishFrame(*frameInfo, instance->mFrameMetricsReporter, frameNumber,
surfaceControlId);
}
}
onSurfaceStatsAvailable与SurfaceFlinger建立关联,是通过SurfaceController,SurfaceFlinger会在acquirceFence触发之后的流程中在独立的线程中回调到CanvasContext。
至此,应用侧的渲染流程就完成了,各个阶段的时间也明确获取到了。
JankTracker又是怎么通过这些时间来确定Jank的类型呢?
首先,Jank Type有这么些:
enum JankType {
kMissedVsync = 0, // 实际的VSync来得比预期的晚
kHighInputLatency, // 输入事件导致卡顿
kSlowUI, // UiThread绘制过久
kSlowSync, // RenderThread从UiThread同步太慢
kSlowRT, // 渲染太慢
kMissedDeadline, // 就是太慢了,这这。。。
kMissedDeadlineLegacy, // 很可能太慢了,有待finishFrame作进一步的判定
// must be last
NUM_BUCKETS,
};
calculateLegacyJank()的任务就是协助finishFrame(),计算出上面几种Jank Type。
作为对比和相互补充,看看SurfaceFlinger侧定义了哪些Jank Type:
// Jank information tracked by SurfaceFlinger(SF) for perfetto tracing and telemetry.
enum JankType {
// No Jank
None = 0x0,
// Jank that occurs in the layers below SurfaceFlinger
DisplayHAL = 0x1,
// SF took too long on the CPU
SurfaceFlingerCpuDeadlineMissed = 0x2,
// SF took too long on the GPU
SurfaceFlingerGpuDeadlineMissed = 0x4,
// Either App or GPU took too long on the frame
AppDeadlineMissed = 0x8,
// Vsync predictions have drifted beyond the threshold from the actual HWVsync
PredictionError = 0x10,
// Janks caused due to the time SF was scheduled to work on the frame
// Example: SF woke up too early and latched a buffer resulting in an early present
SurfaceFlingerScheduling = 0x20,
// A buffer is said to be stuffed if it was expected to be presented on a vsync but was
// presented later because the previous buffer was presented in its expected vsync. This
// usually happens if there is an unexpectedly long frame causing the rest of the buffers
// to enter a stuffed state.
BufferStuffing = 0x40,
// Jank due to unknown reasons.
Unknown = 0x80,
// SF is said to be stuffed if the previous frame ran longer than expected resulting in the case
// where the previous frame was presented in the current frame's expected vsync. This pushes the
// current frame to the next vsync. The behavior is similar to BufferStuffing.
SurfaceFlingerStuffing = 0x100,
};
void JankTracker::finishFrame(FrameInfo& frame, std::unique_ptr<FrameMetricsReporter>& reporter,
int64_t frameNumber, int32_t surfaceControlId) {
calculateLegacyJank(frame); // 优先使用calculateLegacyJank计算一边
// Fast-path for jank-free frames
// 这个总时间是非常合理和明确的
// 它等同于perfetto图上的Expected Time的开始到Actual Time的结束点
int64_t totalDuration = frame.duration(FrameInfoIndex::IntendedVsync,
FrameInfoIndex::FrameCompleted);
// 帧间隔
int64_t frameInterval = frame[FrameInfoIndex::FrameInterval];
// If we starter earlier than the intended frame start assuming an unstuffed scenario, it means
// that we are in a triple buffering situation.
// 三级缓存,现阶段,等于True
bool isTripleBuffered = (mNextFrameStartUnstuffed - frame[FrameInfoIndex::IntendedVsync])
> (frameInterval * 0.1);
// 等同于perfetto图上的Expected Time的结束点
int64_t deadline = frame[FrameInfoIndex::FrameDeadline];
// If we are in triple buffering, we have enough buffers in queue to sustain a single frame
// drop without jank, so adjust the frame interval to the deadline.
// 但是,预想假定可能发生Buffer stuffing,直接延后一个VSync周期
// 笔者认为,这样做有不大合理之处,如果SurfaceFlinger没有判定为Buffer stuffing,这里提前假设,会导致两边的逻辑不一致
// Any way,Jank本身就是一种笼统的判定
if (isTripleBuffered) {
deadline += frameInterval;
frame.set(FrameInfoIndex::FrameDeadline) += frameInterval;
}
// If we hit the deadline, cool!
if (frame[FrameInfoIndex::GpuCompleted] < deadline) {
if (isTripleBuffered) {
mData->reportJankType(JankType::kHighInputLatency);
(*mGlobalData)->reportJankType(JankType::kHighInputLatency);
// Buffer stuffing state gets carried over to next frame, unless there is a "pause"
mNextFrameStartUnstuffed += frameInterval;
}
} else {
mData->reportJankType(JankType::kMissedDeadline);
(*mGlobalData)->reportJankType(JankType::kMissedDeadline);
mData->reportJank(); // 重点:的确发生了Jank,JankType的判定都是有效的
// 笔者:为何不先判断是否Jank,如果没有,那些个Jank Type都不用计算了
(*mGlobalData)->reportJank();
// Janked, store the adjust deadline to detect triple buffering in next frame correctly.
nsecs_t jitterNanos = frame[FrameInfoIndex::GpuCompleted]
- frame[FrameInfoIndex::Vsync];
nsecs_t lastFrameOffset = jitterNanos % frameInterval;
// Note the time when the next frame would start in an unstuffed situation. If it starts
// earlier, we are in a stuffed situation.
mNextFrameStartUnstuffed = frame[FrameInfoIndex::GpuCompleted]
- lastFrameOffset + frameInterval;
recomputeThresholds(frameInterval);
// 重点:这里通过比较器,判断JankType中的剩余几个JankType
// 比较的方法也超级简单,就是时延,如果时延大于等于给定的阈值,归入该类别
for (auto& comparison : COMPARISONS) {
int64_t delta = frame.duration(comparison.start, comparison.end);
if (delta >= mThresholds[comparison.type] && delta < IGNORE_EXCEEDING) {
mData->reportJankType(comparison.type);
(*mGlobalData)->reportJankType(comparison.type);
}
}
}
}
struct Comparison {
JankType type;
std::function<int64_t(nsecs_t)> computeThreadshold;
FrameInfoIndex start;
FrameInfoIndex end;
};
static const std::array<Comparison, 4> COMPARISONS{
// 差一个单位都不行,这个阈值可能有欠缺,实际一般没这么快达到
Comparison{JankType::kMissedVsync, [](nsecs_t) { return 1; }, FrameInfoIndex::IntendedVsync,
FrameInfoIndex::Vsync},
// 0.5个VSync周期
Comparison{JankType::kSlowUI,
[](nsecs_t frameInterval) { return static_cast<int64_t>(.5 * frameInterval); },
FrameInfoIndex::Vsync, FrameInfoIndex::SyncStart},
// 0.2个VSync周期
Comparison{JankType::kSlowSync,
[](nsecs_t frameInterval) { return static_cast<int64_t>(.2 * frameInterval); },
FrameInfoIndex::SyncStart, FrameInfoIndex::IssueDrawCommandsStart},
// 0.75个VSync周期
Comparison{JankType::kSlowRT,
[](nsecs_t frameInterval) { return static_cast<int64_t>(.75 * frameInterval); },
FrameInfoIndex::IssueDrawCommandsStart, FrameInfoIndex::FrameCompleted},
};
void JankTracker::calculateLegacyJank(FrameInfo& frame) REQUIRES(mDataMutex) {
// Fast-path for jank-free frames
int64_t totalDuration = frame.duration(sFrameStart, FrameInfoIndex::SwapBuffersCompleted);
if (mDequeueTimeForgivenessLegacy && frame[FrameInfoIndex::DequeueBufferDuration] > 500_us) {
// DequeueBuffer如果大于500us,说明可能有问题
nsecs_t expectedDequeueDuration = mDequeueTimeForgivenessLegacy
+ frame[FrameInfoIndex::Vsync]
- frame[FrameInfoIndex::IssueDrawCommandsStart];
if (expectedDequeueDuration > 0) {
// Forgive only up to the expected amount, but not more than
// the actual time spent blocked.
nsecs_t forgiveAmount =
std::min(expectedDequeueDuration, frame[FrameInfoIndex::DequeueBufferDuration]);
if (forgiveAmount >= totalDuration) {
ALOGV("Impossible dequeue duration! dequeue duration reported %" PRId64
", total duration %" PRId64,
forgiveAmount, totalDuration);
return;
}
totalDuration -= forgiveAmount;
}
}
// 理论一,渲染应该在一个VSync周期完成,如果达不到这个性能,标记一下
if (totalDuration > mFrameIntervalLegacy) {
mData->reportJankLegacy();
(*mGlobalData)->reportJankLegacy();
}
// 计算一个swap的截止时间
if (mSwapDeadlineLegacy < 0) {
mSwapDeadlineLegacy = frame[FrameInfoIndex::IntendedVsync] + mFrameIntervalLegacy;
}
bool isTripleBuffered = (mSwapDeadlineLegacy - frame[FrameInfoIndex::IntendedVsync])
> (mFrameIntervalLegacy * 0.1);
mSwapDeadlineLegacy = std::max(mSwapDeadlineLegacy + mFrameIntervalLegacy,
frame[FrameInfoIndex::IntendedVsync] + mFrameIntervalLegacy);
// If we hit the deadline, cool!
// 在Deadline前完成,很好,否则判定为Input事件导致的Jank,JankType::kHighInputLatency
// 笔者的疑问:为什么没有可能是GPU性能不足呢??
if (frame[FrameInfoIndex::FrameCompleted] < mSwapDeadlineLegacy
|| totalDuration < mFrameIntervalLegacy) {
if (isTripleBuffered) {
mData->reportJankType(JankType::kHighInputLatency);
(*mGlobalData)->reportJankType(JankType::kHighInputLatency);
}
return;
}
// 如果找不到原因,则是应用侧慢的问题,应用的问题?
mData->reportJankType(JankType::kMissedDeadlineLegacy);
(*mGlobalData)->reportJankType(JankType::kMissedDeadlineLegacy);
// Janked, reset the swap deadline
// 一旦Janked,更新swap的截止时间
nsecs_t jitterNanos = frame[FrameInfoIndex::FrameCompleted] - frame[FrameInfoIndex::Vsync];
nsecs_t lastFrameOffset = jitterNanos % mFrameIntervalLegacy;
mSwapDeadlineLegacy = frame[FrameInfoIndex::FrameCompleted]
- lastFrameOffset + mFrameIntervalLegacy;
}
Jank类型的逻辑,直接看上面代码的注释吧,其中,计算比较复杂的部分类似SurfaceFlinger,需要特别考虑Buffer stuffing。
小结,JankType判断大致逻辑:
enum JankType {
kMissedVsync = 0, // 实际的VSync来得比预期的晚
kHighInputLatency, // 输入事件导致卡顿
kSlowUI, // UiThread绘制过久,超过了0.5个VSync周期
kSlowSync, // RenderThread从UiThread同步太慢,超过了0.2个VSync周期
kSlowRT, // 渲染太慢,超过了0.75个VSync周期
kMissedDeadline, // 就是太慢了,acquireFence没有在期望的时间之前触发
kMissedDeadlineLegacy, // 很可能太慢了,有待finishFrame作进一步的判定
// must be last
NUM_BUCKETS,
};
GraphicsStats
这个仅做提示,GraphicsStats是一个系统服务,利用ProfileData与CanvasContext中的JankTracker建立关联,具体东西就略过了。
可以通过 adb shell dumpsys graphicsstats 来查看这个package的Jank统计信息。
总结
通过追踪应用各个步骤的耗时,JankTracker/FrameInfo给出了应用绘制问题导致Jank的更详细的分类,用来补充FrameTimeline的不足。
如果我们将JankTracker得到的FrameInfo信息传递给SurfaceFlinger,必定能在发生Jank时提供更加详尽的Jank归因。
参考
http://www.aospxref.com/android-13.0.0_r3/xref/frameworks/native/
http://www.aospxref.com/android-13.0.0_r3/xref/frameworks/base/native/
http://www.aospxref.com/android-13.0.0_r3/xref/frameworks/base/libs/hwui/